Hierarchical Perceiver
Problems
- Perception Models are able to process large inputs and largely focused on Global attention.
- Fourier embeddings must be adjust to fit the modality of data and become memory bottleneck when dealing with high dimensional data
Novelties
- This paper shows that by introducing some degree of locality, it can improve the efficiency of perceiver model.
- Masked Auto-Encodign(MAE) plays a mojor role in learning positional embeddings
Architecture
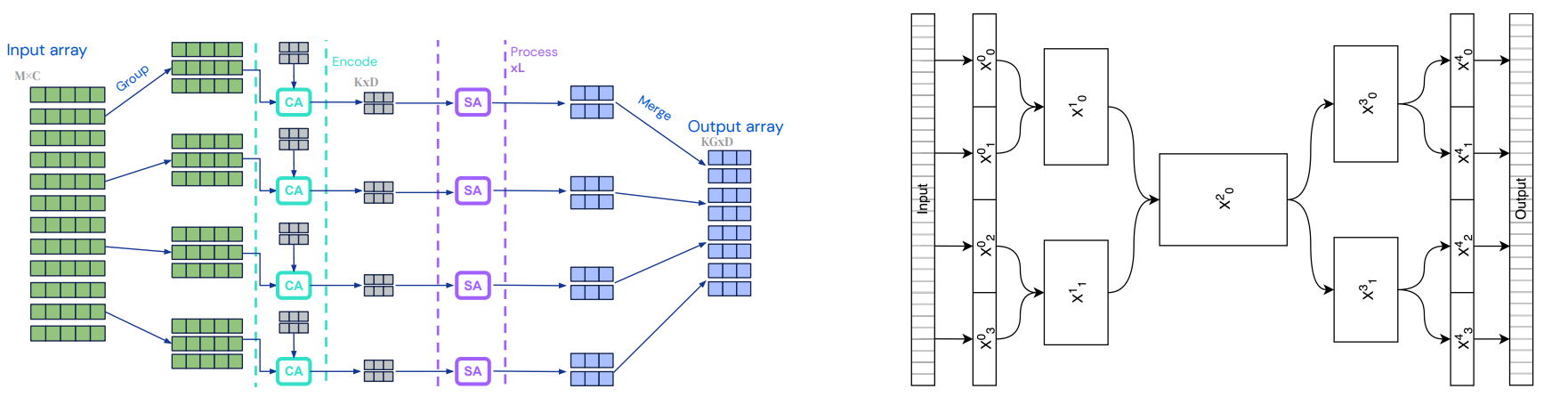
Input data is assumed to be processed such that it is in a shape of M x C where M is number of tokens and C is number of channels
Input data is then grouped into G groups each with M/G tokens. Note that G is fixed for each layer and each group has its learned latent features of shape K x D where K is number of latent vectors and D is number of latent vector channel.
In each group, input data is cross attended to latent vectors to form output of shape K x D.
The output of cross attention is then attended through a few layers of (Self Attention and MLP, ie typical Transformer Layer).
The output of each group is then merged and be the input of next block.
Input data is flatten, yes reshape to 1-D, this works for all modalilty of data and preserves part of the locality.
Results
- Although it is not SOTA on ImageNet, but the performance is not far behind, consider SOTA models have large hand-crafted layers specifically for images.
- Flattening or Local structure is important.
- MAE learn rich low-dimensional positional embeddings. Classification is a sparsely supervised downstream task which is not sufficient for model to learn rich representation unlike MAE.
- For point cloud data, pretraining using MAE yields much better result although no visible structure is observed in the learned positional embedding.